Fill Your IRS 941 Template
The IRS Form 941 is a quarterly tax form that employers use to report income taxes, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax withheld from employee wages. This form is essential for keeping track of payroll tax obligations and ensuring compliance with federal tax laws. To learn more about how to fill out the form correctly, click the button below.
Make My Document Online
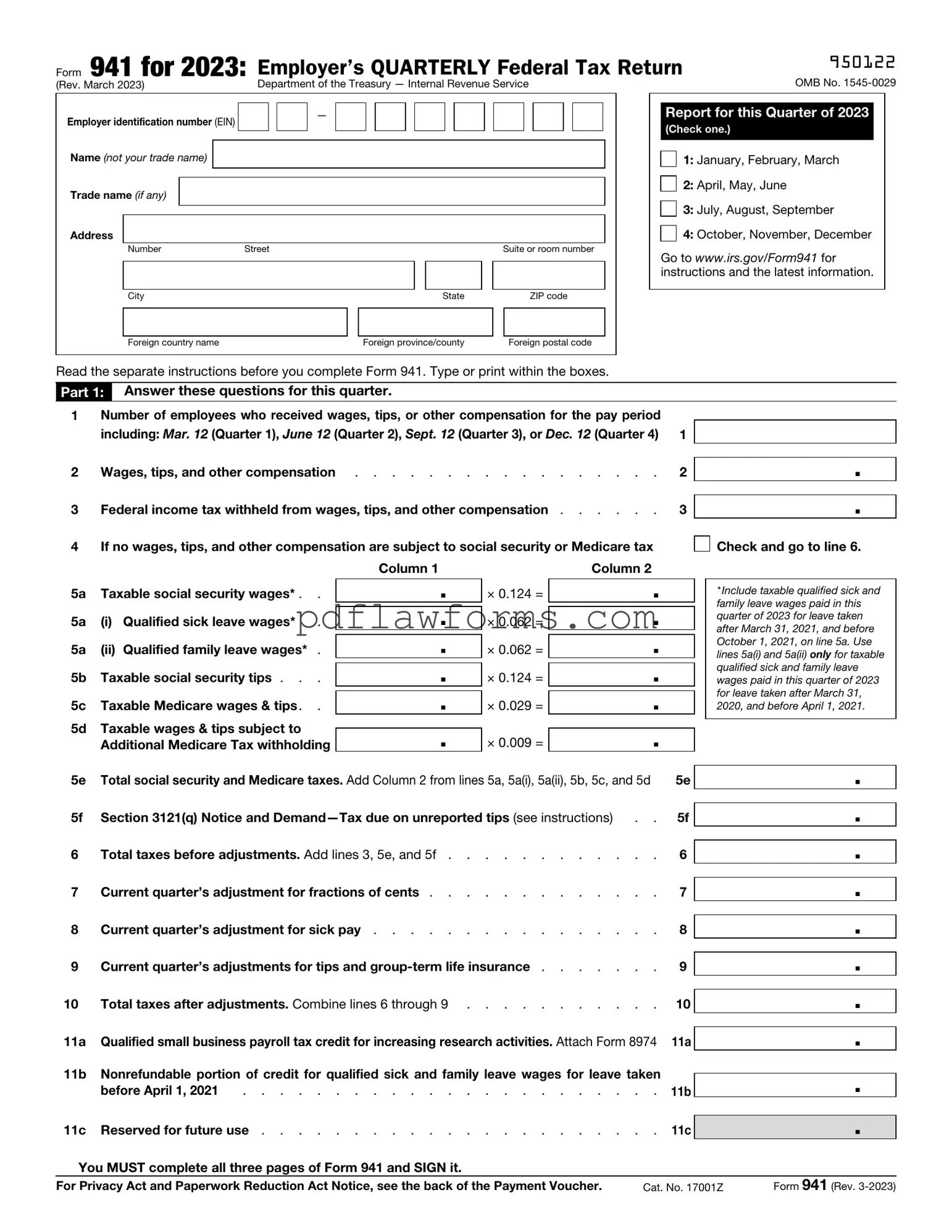
Fill Your IRS 941 Template
Make My Document Online
You’re halfway through — finish the form
Edit and complete IRS 941 online, then download your file.
Make My Document Online
or
⇩ IRS 941 PDF
